High refractive index dielectric nanostructures that support electric and magnetic resonances have emerged as new building blocks in nanophotonics for novel functionalities.
By arranging these nanostructures periodically, the coherent interference between the localized Mie resonances of individual nanostructures and the in-plane diffracted light can lead to the so-called Mie surface lattice resonances (SLRs).
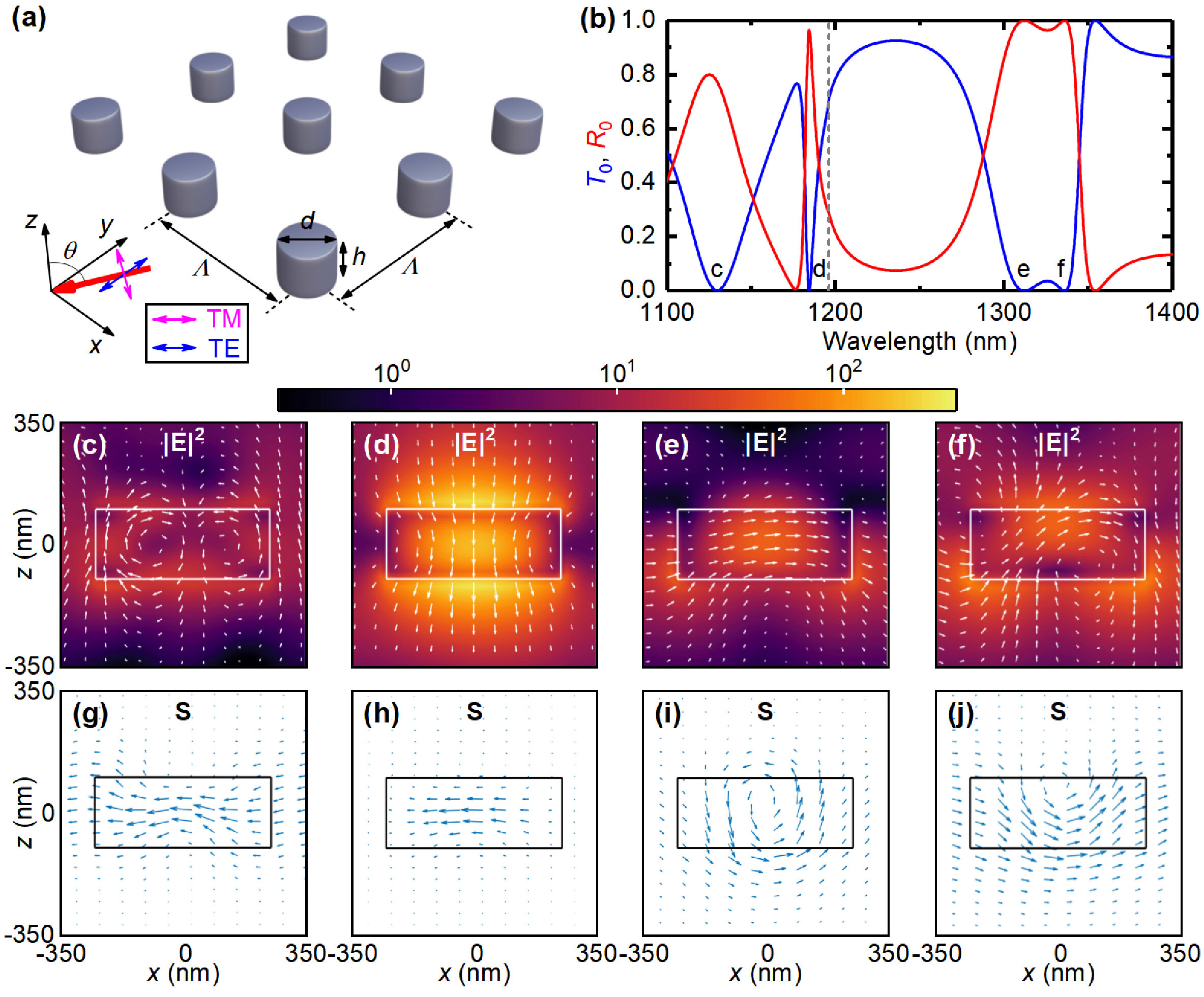
Researchers at the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences studied the periodic silicon nanodiscs under oblique incidence with transverse magnetic polarization and detected out-of-plane Mie dipole surface lattice electric resonance (ED-SLR) for the first time.
The study was published in Optics Express on Sept 7th
The team discovered the out-of-plane Mie ED-SLR along with the in-plane electric dipole SLR (ED-SLR), magnetic dipole SLR (MD-SLR), and magnetic quadrupole SLR (MQ-SLR). periodic silicon nanodiscs could be excited under oblique incidence. They found that the out-of-plane Mie ED-SLR could have four times greater quality factors than the in-plane camera under the same conditions.
Li’s team noted that unlike the plasmonic out-of-plane ED-SLR, which is a subradiant or dark mode, the out-of-plane Mie ED-SLR can be treated as a light mode and has a Distinctive near-field optics has distributions and dispersion relationships.
“This is because the dipole field for Mie ED-SLRs is induced by displacement currents and the plasmonic ED-SLRs are induced by free electron gases,” said Dr. Li Guangyuan, corresponding author of the study.
Researchers also found that the out-of-plane Mie ED-SLR can define a symmetry-protected bound state in the continuum at normal incidence. This is because the out-of-plane Mie ED-SLR is not allowed to emit at normal incidence. At small angles of incidence, the quality factor can even reach 104.
“This work offers a new approach to achieve ultra-high quality factors of Mie SLRs in dielectric metasurfaces,” said Dr. Li. “In addition, the coexistence of multipole SLRs opens up new perspectives for the manipulation of light-matter interactions.”
Dual Grid Kerker Effects: Control of light scattering with incident polarization and incident angle
Xueqian Zhao et al, High-Q out-of-plane Mie electric dipole surface lattice resonances in silicon metasurfaces, Optics Express (2022). DOI: 10.1364/OE.471356
Provided by the Chinese Academy of Sciences
Citation: Researchers Discover a New Type of Surface Lattice Resonance (2022 September 13) Retrieved September 14, 2022 from https://phys.org/news/2022-09-surface-lattice-resonance.html
This document is protected by copyright. Except for fair trade for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without written permission. The content is for informational purposes only.
#Researchers #discover #type #surface #grating #resonance

Leave a Comment